In comparison, the true story of Mars and humans is less romantic, but its beauty does not detract from it. The telescope's observation turned the bright red dots in the sky into a fuzzy, mottled dish that created the day-long fantasy of a canal on Mars. Just 50 years ago, a spacecraft on Mars captured its first photograph showing Mars has a blurry atmosphere. Now, after decades of exploration by Mars, it has been discovered that Mars once existed in open waters - the basic elements of the existence of life.
Even in the Internet age, people's obsession with Mars has not faded. Andy Weir, a former programmer who is passionate about writing and happily blogging his science fiction, has serialized the story of a NASA astronaut running aground. The story was so popular that eventually Andy Will adapted it into a successful novel, Mars Rescue, whose movie of the same name was released in October 2015.
Mars Amalgamated the imagination and facts about Mars and built the story on NASA and other organizations working together to explore Mars and pushing the passage of time to 2030 - when NASA astronauts Will regularly board Mars and live on the surface of Mars for a period of time to carry out exploration work. Although 20 years after the novel's story took place, NASA actually has many of the technologies that appear in the movie.
Habitat
On Mars, Watney spends much of his time in the dwelling, away from home. Future astronauts landing on Mars will also need such a home, otherwise, astronauts have to wear spacesuits, lying in the dust to spend their Mars time.

NASA's Human Exploration Research Simulator (HERA) is an independent space that simulates an outer space capsule. This two-storey space consists of a living area, work area, hygiene cabin and a simulated airlock. Among them, the test subjects need to perform operational tasks, complete the load targets, and co-exist for 14 days (soon to increase the plan to 60 days), simulating future tasks in an isolated environment. Astronauts are also using this facility to simulate the ISS mission recently. These simulations provide valuable data on human factors, behavioral health, and coping with issues that can help deepen NASA's understanding of how to conduct missions for outer space exploration in the future.

Plant Farm
Currently, the International Space Station astronauts can get enough food from the cargo replenishment spacecraft, some spacecraft or commercial companies. But on Mars, people can not rely on earth to get food - it takes at least nine months, even for the quickest way to get it. If people want to survive on Mars, they need a constant source of food. Therefore, they will need to grow their own crops.


In Mars Rescue, Watney turned his cabin into a self-sufficient farm, and potatoes became the first major agricultural product on Mars. Now, near the Earth's Earth orbit, lettuce is the most abundant crop. There is a set of applicable fresh food production systems at the International Space Station: "Veggie". Using red, blue and green light, the Veggie project allows plants to grow on "pillows" - sachets containing media and fertilizers, capillaries on the surface and harvested by astronauts. In 2014, astronauts succeeded in planting "Outredgeous" red romaine lettuce through this system, which was recently tasting the cosmic vegetable for the first time. This is a major step forward in space planting, and NASA also hopes to further expand the number and variety of crops to meet the nutritional needs of future astronauts landing on Mars.

Water Recovery
There are no lakes, rivers or oceans on the surface of Mars, and it takes nine months or more if water passes over Earth. Astronauts on Mars must create their own water system. Because of the water recovery device on the 3rd Ares, all members of the spacecraft did not waste a drop of water on Mars, and Watney needed to rely on his intelligence to ensure he was not dehydrated on this red planet, And survive.
In the International Space Station, there is no sweat, tears and even urine will be wasted. Environmental Control and Survival Systems collect and recycle water collected from a variety of sources: urine, hand-washing water, water used for oral hygiene, and more. Through WRS, water is recovered, filtered and put back into service. An astronaut once said: "Yesterday's coffee is today's coffee."
In space, liquids do pose some tough problems. Related systems such as water recovery systems must take into account that liquids behave very differently in the microgravity space. For example, centrifuges must be used in the water recovery system to process the urine because liquids and gases do not separate in space as they would on Earth.
NASA has not stopped the pace of research and development of new technologies for water recovery. At present, research is trying to improve the performance of disposable multi-purpose filters (used to filter inorganic pollutants and non-volatile organic pollutants), making them more permanent components in water recovery systems. The brine recovery process will recover each drop of water from the "bottom" of the urine distillation. In future exploration missions, astronauts will have less reliance on supplies of water and parts from the Earth.
The technology has also been introduced to some remote areas of the planet or areas hit by severe natural disasters to provide them with clean drinking water.
Oxygen Generation
Water, Food, Shelter: They are the three basic elements that survive the earth. Yet another fourth element is often overlooked by us because on Earth the elements are always available for free - oxygen. On Mars, Watney could not run outside and breathe in fresh air. To survive, he must bring his own oxygen supply with him wherever he goes. But first, he has to make his own supply. In his cabin, he used an "oxygenation machine," a tool used to make oxygen from carbon dioxide enriched in fuels from the MAV.
At the International Space Station, astronauts have an oxygen generation system that reprocesses the air in the space station to efficiently and sustainably provide astronauts with breathable air. This device through the electrolysis process, the water molecules in the hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms separated. Oxygen is released into the air and hydrogen is discarded into the universe or into the Sabatack system, a system that extracts water from the by-products of the station's atmosphere.
Mars Spacesuit
Mars surface may not be suitable for humans. The atmosphere there is very cold and there is almost no air to breathe. Aerospace suits are essential to astronauts who want to survive when collecting samples of the Mars surface outside the living quarters and maintaining the facilities.


Mark Waters, who often works in spacesuits on his Sol day, a sunrise-sunset cycle on Mars, will eventually need to travel long distances on Mars. Therefore, his spacesuit should be flexible, comfortable and reliable.
Now NASA is studying spacesuit technology that can be used to explore the planet. From crossing the Martian landscape to collecting rock samples, design engineers need to take into account everything that astronauts need to do on Mars.
The Z-2 and Prototype eXploration space suits, NASA's new cosmodrome sample, use new technologies to solve unique problems that will be used in the future by the first astronauts on Mars Aerospace suit. They are used to solve different technical gaps - that is, the missing functions of the space suit in completing Mars missions. Spacesuit design engineers weigh the hard composites and fibers to find the balance between durability and flexibility.
One of the great challenges of walking on Mars is the dust on Mars. After walking on the surface of Mars, the red soil of Mars, if it is brought into spacecraft, can have an impact on astronauts and cabin facilities. To deal with this issue, the new spacesuit has been designed with a suit port on the back so that astronauts can quickly jump into the spacesuit from inside the cabin leaving the spacesuit outside of the cabin, keep clean.
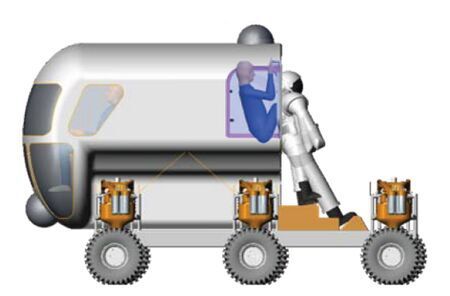
Rover
When people land on Mars, they spend at least a year on Mars waiting for Mars and Earth to move to their nearest spot. This gives astronauts plenty of time to experiment and explore the surroundings, however, they will not be willing to limit the scope of their exploration to areas within walking distance. Therefore, astronauts need to use more robust, reliable and versatile rovers to travel further afield.
Watney ran several times over his rover in "Mars Rescue," and even did less orthodox modifications to his rover to survive.


Today, on Earth, NASA is using the Multi-Mission Space Exploration Vehicle (MMSEV) to prepare for any situation it may encounter. MMSEV has been used in NASA's mock mission programs to help address issues already known to NASA and to discover issues that have not been identified. The technology is versatile and can be used to support future exploration of asteroids, Mars, Mars satellites and other types of missions. At present, MMSEV has played a role in solving problems such as driving distance, rapid access and radiation protection. In order to ensure the detector mobility, some versions of the detector equipped with six steering wheels. In this way, even with a flat tire, the rover can still function as long as the tire is stowed upwards.
Ion Propulsion
In Mars Rescue, astronauts on the 3rd God of War spent a few months on the Hermes spacecraft traveling to and from Mars, using an effective propulsion of the ion engine across the Nearly 500 million kilometers of space. The ion engine works by energizing argon or xenon to release ions at a speed of about 350,000 kilometers per hour. The spacecraft receives the force of a gentle, gentle breeze, but with years of continued acceleration, the spacecraft can eventually reach alarming rates. ION also allows the spacecraft to change its orbit a number of times, and then off track, toward another distant world.

This technology enables NASA's spacecraft today, such as the Dawn Detector, to minimize fuel consumption and perform some crazy orbit changes. The dawn has now completed a sustained acceleration of more than five years, with a cumulative speed change of 40,000 kilometers an hour, surpassing any spacecraft propelled by its own propulsion system alone. Along the way, it completed the first human visits to the dwarf star Vesta and the asteroid Ceres.
Solar Panels
There are no gas stations on Mars, no power plants, and almost no wind energy. For the manned mission on this red planet, solar energy can help the astronauts. In Mars Rescue, the Hermes spacecraft used solar arrays to generate electricity, and Mark Watney had to take some unconventional ways to use solar panels to survive.

At the International Space Station, four solar arrays generate between 84 and 124 kilowatts of power - enough to power forty people. Space stations do not require as much energy, but if something goes wrong, redundancy can help reduce risk. The space station solar power system is very reliable, since the first astronauts landed in 2000 so far, the space station has been safely provided to the astronauts of electricity.
NASA's Orion spacecraft, a spacecraft that will take people to an unprecedented distance - will also use solar arrays for future missions. In the sun, the battery array can collect energy to charge lithium-ion batteries on board. In the absence of sunlight - such as when running behind the moon - there will still be enough energy for Orion spacecraft to operate.

Radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG)
For more than 40 years NASA has safely used radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to power more than two dozen missions, including the Apollo missions to the moon. Spacecraft such as the Curiosity rover and the upcoming Mars 2020 detector are based on a new generation of improved power generation.
RTG is a "space battery" that converts the natural radioactive decay of plutonium-238 into reliable electricity. RTG on Curiosity produces no more than 110 watts of power - just slightly above the power needed for a normal light bulb.
In Mars Rescue, astronauts buried plutonium-based RTG energy far away from their homes to prevent a nuclear leak. As the movie said, in order to avoid any possible leaks, Pu-238 itself has several layers of solid and advanced materials that will not leak even after a serious accident. The RTG primarily emits alpha rays, which move only a few centimeters in the air and do not penetrate clothing or human skin. It is harmful to human health only if it is broken down into particles or evaporated and inhaled or ingested. This isotope is made in ceramic form, in particular, it is insoluble in liquids and therefore the likelihood of inhalation and ingestion is virtually negligible.
In reality, the natural radiation of the Martian environment is much greater than the radiation produced by the RTG. Ionizing radiation rain falling from outer space on Mars is also more detrimental to human health. Currently, NASA's Mars mission is also analyzing the radiation environment on Mars, allowing mission planners to design protective measures for future astronauts.
Future explorers need to ensure that they have a viable and lasting source of energy before they reach Mars. The power system may include a series of combinations of more efficient radioisotope power generation systems, solar energy, fuel cells and nuclear fission.
Mars journey
Manned space is a dangerous business. NASA plans to send humans to Mars in the 1930s, but until then, many milestones will need to be achieved if astronauts return safely to Earth. Scott Kelly, an astronaut who has now lived on the International Space Station for the better, concludes: "Space is a dreadful space, and for each level of spaceflight, the margin of error is almost Close to zero.However, in the journey to Mars, we have a deeper understanding of the universe; everything we have learned and brought back will ultimately benefit all humankind. "
Original Source: http://luxury.msn.com.cn/jewelleryandwatch/jwshare/443958.shtml
Concrete Wire Mesh,Square Wire Mesh,Welded Wire Mesh
Yeson International Trading Co., Ltd. , http://www.jssteelsheet.com
没有评论:
发表评论